Structured Cabling Philippines
Structured cabling is a term used for cabling and related components in a logical and ordered way. Structured cabling involves standardized smaller elements called subsystems. It separates different types of cabling.
A cabling system though looks like the most simple component and less complex at first look, it should not be underrated as if we don’t lay a cable properly , it can cost us a lot in terms of downtime and most of the outages or network issues often come due to unstructured and clumsy cabling. With the increasing needs of network equipment and servers in our datacenters, unstructured cabling would bring in more losses than any other problem in a network.
Structured cabling has predefined industry standards and we completely adhere to the industry standards. It should also meet local building and electrical codes.
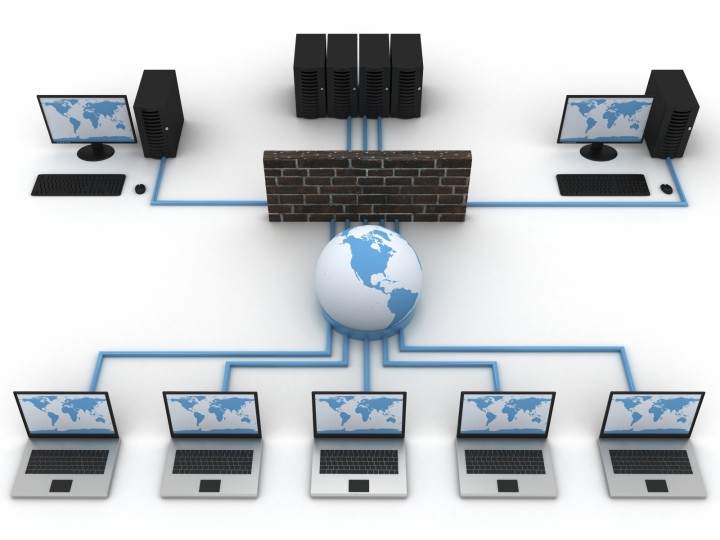
Structured cabling refers to a cabling infrastructure of a campus or a Datacenter. The common components of a structure cabling are:
- Demarcation point : a juncture between the telecom company/ISP and our campus/DC
- Main Distribution Frame (MDF) : The location where the ISP system and main components of our network infrastructure.
- Intermediate Distribution Frames (IDF): locations where the end user connecting equipment and wiring is placed at different floors of the building. Generally not needed in smaller office where there are less than 100 employees and just a single floor or section of a floor.
- Horizontal wiring: This refers to the cabling that connects MDF and IDFs.
The common type of cables that are used in horizontal wiring would be cat3, cat5e, cat6, coax and fiber optical cables.
Structured cables look a lot better and easy to track as compared to Here are the solutions we offer:
- Cabling for Data
- Cabling for Voice
Structured cabling for Data
- Data cabling refers cabling done for connecting data network infrastructure. It involves components such as firewalls, routers, load balancers, servers and switches handling data traffic.
- Data traffic has different needs and some data can wait at times until and unless it’s of high priority. ( e.g. : a payment gateway data should be of high priority )
- We generally use Cat5e or fiber optic cables based on the requirement ( also use Coax for ISP end links )
- Most Data links will be a mix of cost effectiveness and quality. As based on the criticality we can use copper cables too and with the high speed copper cables in the market, we can get match the speed requirements without fiber too.
Structured cabling for Voice
- Voice cabling is a little different that data. It generally involves equipment like PSTN, phones, IP phones, Call managers and SIP/SCCP servers.
- Voice traffic should be separated from the data traffic as it increases the efficiency of voice traffic as well as gives enough space to the data traffic with a separate VLAN architecture.
- We can use different cables depending on the requirement for voice cabling. We can use fiber where highest quality is expected and we can also use Cat5e or Cat6 cables in the DC. From an ip phone towards the call manager, copper cabling is a good option.
- With Voice cabling, quality has to be kept above the cost effectiveness always. We need to explore ways to reduce the bandwidth from a technology front rather than using low cost cables.
Structured cabling always helps in saving cost in a long term basis as well as very easy to manage from administration point of view. We recommend separate cabling and VLAN for voice and data as it would increase the performance of each type of traffic. It also makes life easy for the network administrators as they have dedicated cabling and infrastructure for their equipment based on the Line of Service. ( say data and voice )
